Dogs have been our faithful friends for millennia, and their human language is nothing short of remarkable. We can use barks and wagging tails to figure out what dogs are saying, but dogs also speak in a wide range of less obvious and less familiar ways. Here we’re diving into the wonderful canine communication realm, to uncover some uncanny ways in which dogs express their feelings, desires, and needs. Get ready to get to know your four-legged friend better and strengthen your relationship like never before.
1. The Language of Sniffs
The Power of the Canine Nose
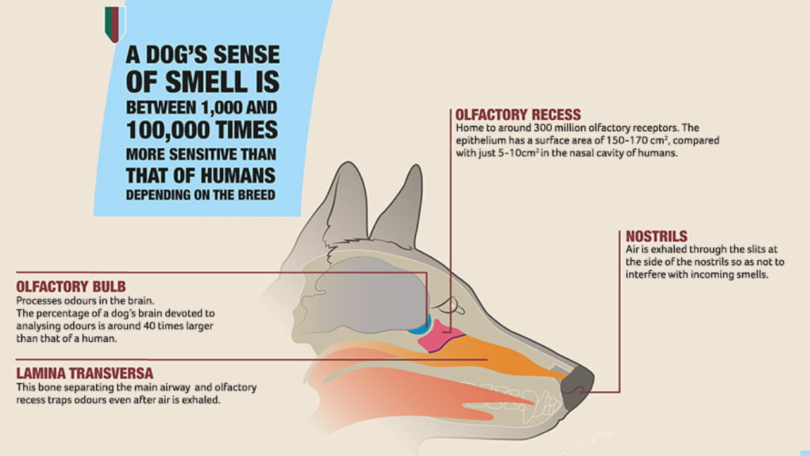
Dogs know everything mainly through their noses. They have this great sense of smell that helps them learn things and speak to you in ways you’d never guess.
Scent Marking
Territorial Marking: Dogs urine on objects to mark territory. That scent sign indicates their presence and rank to other dogs.
Social Details: The scent traced can tell you what age, sex, condition, even state of emotion the dog is in.
Greeting Rituals
Dogs usually sniff one another’s hind legs when they come together. We may be puzzled by this behaviour, but it’s also a fine way of communicating.
- Scent Glands: The odour glands at the anus of a dog create distinctive odours, that convey a lot.
- Social Hierarchy: Sniffing lets dogs perceive each other’s social status and motives.
2. The Silent Language of the Body: Body Language.
Reading the Signs
The dog knows best how to communicate via body language, and his body can be used to convey an entire host of feelings and intents. So if you’re paying attention to these cues, you can learn how to read your dog’s movements.
Tail Wagging
- Position and Speed: A high, rapid wag will signal tension, a slow, low wag could mean insecurity or submission.
- Direction: Some studies show that the wag on the right is related to positive feelings, whereas the wag on the left can be negative.
Ear Position
- Piqued: Rounded ears indicate excitement and vigilance.
- Pinned Back: Flattening ears against the head is an expression of fear, deference or discomfort.
Eye Contact
- Soft eyes: Soft eyes point to a relaxed, happy dozg.
- Hard Stare: A hard, intense stare can indicaete violence or authority.
3. The Expressive Face
Beyond the Puppy Dog Eyes
Dogs have various expressions that let us know how they feel. Getting an understanding of these words can give you useful information about how your dog feels.
The “Dog Smile”
- Relaxed Mouth: An open slightly relaxed mouth with relaxed lips can mimic a smile and is often a sign of a relaxed happy dog.
- Panting: While panting might signal sweat or fatigue, a loose pant with a soft smile is a mark of contentment.
Raised Eyebrows
Curiosity and Concern: Dogs don’t shy away from a raised eyebrow when they have something to be curious or concerned about. This term is for helping them learn more about the world.
4. The Language of Touch
Physical Contact as Communication
Dogs use contact to communicate with their owners and other dogs. These gestures can help you respond to your dog’s needs in a way that makes sense.
Leaning
- Seeking Consolation: if a dog sits on your back, it is usually to be for consolation and safety.
- Love: Leaning is also a way that dogs express love and affection towards their humans.
Pawing
- Playing & Excited: Dogs will always use their paws to capture your attention, whether that is to play, go outside, or simply get love.
- Reassurance and Reassurance: Pawing can also be used for dogs to find relief and reassurance from their owners.
5. The Mystery of Vocalizations
Beyond Barking
Barking is the most obvious form of vocalization, but dogs communicate with different sounds.
Whining
- Pain or Stress: When dogs whine, they are indicating that they are nervous, uneasy, or need something.
- Attraction-Seeking: Dogs can also bark to be picked up or to show excitement.
Growling
- Alert: Growling is normally a sign that a dog feels threatened or uncomfortable.
- Play: Sometimes dogs growl while playing, and that can be deceiving. : Take the context and body language in your hand to make the growl sound right.
Howling
- Language: Howling is a language that can communicate with each other far away, acquired from wolves. Dogs might bark to call out to other dogs or in response tao stimuli.
- Needing Attention: Some dogs howl to attract attention from theiur owner or show lonely.
6. The Significance of Tail Position
Decoding the Tail
A dog’s stance at the tail can tell you a great deal about his mood and intentions. If you learn to interpret these cues, then you’ll have a much easier time figuring out what your dog is doing.
High Tail
High Tail Confidence and Awareness: A high tail suggests confidence and awareness. It usually occurs when dogs are preoccupied or over-excited.
- Aggression: Sometimes aggression is indicated by a long, stiff tail.
Low Tail
- Subjection and Fear: A low tail, ideally wedged between the legs, means submission, fear, or anxiety.
- Relaxation: A dangling tail can also suggest a calm, satisfied dog.
Wagging Tail
Excited and Happy: A wagging tail will normally indicate excitement and happiness, but the context and body language are key to correct interpretation.
7. The Role of Play Behavior
Play as Communication
Play is a fundamental part of a dog’s existence and a language. Play behaviour can be useful in assisting you to relate to your dog and what they need.
Play Bow
- Invitation to Play: The play bow (when a dog lowers its front legs and lifts its hindquarters) is clearly an invitation to play.
- Prompts of Goodwill: This expression suggests that you’re propping up for a social encounter.
Chasing and Wrestling
- Socialization: Chasing and wrestling are routine play games that make dogs socialize and build their social hierarchies.
- Burning Off Energy: Play helps dogs burn off energy and develop social skills.
8. The Importance of Routine
Predictable Patterns
Dogs love routine and communicate through it. Taking into account your dog’s need for routine can provide a stable and secure space.
Mealtime Rituals
- Expectation: Dogs can become excited or anxious at mealtimes, signaling they are hungry and anxious.
- Reliability: Keeping up with a regular feeding routine keeps dogs feeling safe and less anxious.
Walk and Playtime
- Exercise: Regular exercise and playtime are essential for the body and berain of a dog.
- Bonding: There arne also activities during these that allow you to bond and communicate with your dog.
9. The Impact of Environment
Environmental Influences
The dog’s surroundings affect his or her behavioral and verbal behavior. By getting to know these influences, you’ll be able to create a healthier and more nurturing home for your dog.
Sensory Stimulation
- Aromas and Noises: Dogs are incredibly picky about smells and sounds. Adding a range of sensory inputs can keep them occupied and alert mentally.
- Security Areas: Providing safe, quiet areas for your dog will prevent stress and anxiety.
Social Interaction
- Human Companionship: Dogs are social creatures who love being with human beings. It creates an instant bond and communication between you and your dog by spending quality time together.
- Dog companions: Socialization with other dogs is equally beneficial for the welfare of a dog and the formation of proper social skills.
10. The Science of Empathy
Emotional Connection
Dogs are so clever at feeling what’s going on with humans. Knowing about this emotional connection can make you better able to meet your dog’s needs and maintain the relationship.
Mirroring Emotions
- Emotional Infection: Dogs resemble their owners’ feelings, listening for slight signs and acting accordingly.
- Consolation: Using this empathy, dogs can comfort and console owners when they’re feeling sad or overwhelmed.
Training and Bonding
- Positive Reinforcement: Positive reinforcement builds trust and strengthens your dog’s emotional connection with you.
- Clear Communication: Repeated and consistent communication informs dogs of what is expected and minimizes confusion.
When we are exposed to these unexpected dog-to-dog communication practices, we understand more about how full and layered canine communication really is. From body language to the impact of smell, dogs have a variety of ways to communicate with us.
Knowledge of these communication channels not only helps us get along better with our furry loved ones, but allows us to meet their needs more efficiently. From understanding the meaning of a tail wag, to reading a play bow, to appreciating the humanity of a lean that soothes, every action and reaction conveys an account of our dog’s thoughts and intentions.
When we keep watching and learning, we discover more about the canine language and develop a more intimate and satisfying relationship with our dogs. So the next time your dog suckles, wavers his tail, or gives you that lovely head-sway, remember that they’re expressing themselves in a language full of meaning and emotion, and you’re invited to enter their world.



Leave a Comment